Diets & Meal Plans
4 types of foods to avoid for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia
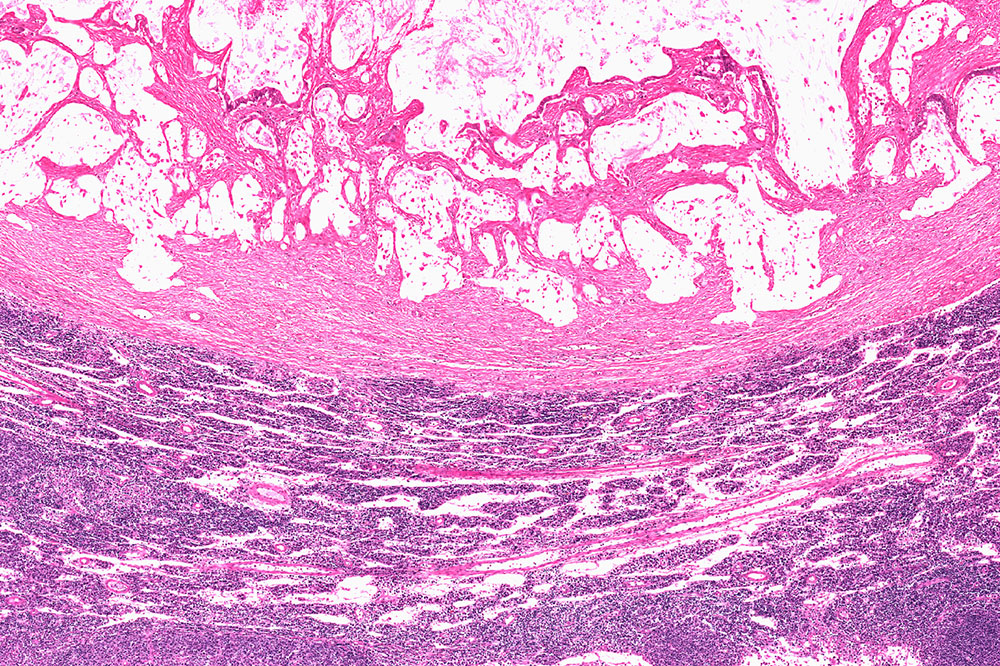
Chronic myeloid leukemia or CML is a type of blood cancer caused due to genetic mutation of blood-forming cells called myeloid present in the bone marrow. Oncologists estimate that 15% of leukemia is of type CML. While there are treatments that can inhibit the disease, avoiding the following foods can help one better manage CML. Uncooked food Since leukemia is a type of blood cancer, it can cause various blood cell deficiencies like leukopenia and neutropenia. Unwashed, uncooked, or undercooked vegetables and fruits have dirt, pesticides, and other contaminants. Ingestion of the same can weaken the immune system. Blood deficiencies can make it difficult for the body to fight infections, making disease management difficult. Similarly, it is imperative to wash and cook raw meat properly to kill bacteria or any other pathogen that can be harmful to the body. Deli meat Deli meats such as sausages, ham, corned beef, beef jerky, bacon, and other frozen meats contain preservatives that increase shelf life. Oncologists suggest that these preservatives can be used by cancerous cells as fuel, which can accelerate their growth in the blood. This can be counterproductive even if the patient is undergoing treatment to suppress the growth of chronic myeloid leukemia. It is also recommended to avoid consuming raw eggs (runny yolk) and foods containing the same such as homemade mayonnaise and raw cookie dough. Processed foods Like deli meats, packaged foods such as chips, frozen pizza, ice creams, canned tuna, crackers, and even granola bars contain food additives like preservatives and taste enhancers. These lock their flavor for longer and increase their shelf life. However, these ingredients are harmful to a CML patient who is already suffering from blood deficiencies. Hence, it is highly recommended to eat freshly cooked food. Gluten Gluten is a type of protein found in whole grains like wheat, barley, and rye.