Health
Acute GvHD – Signs, diagnosis, and management
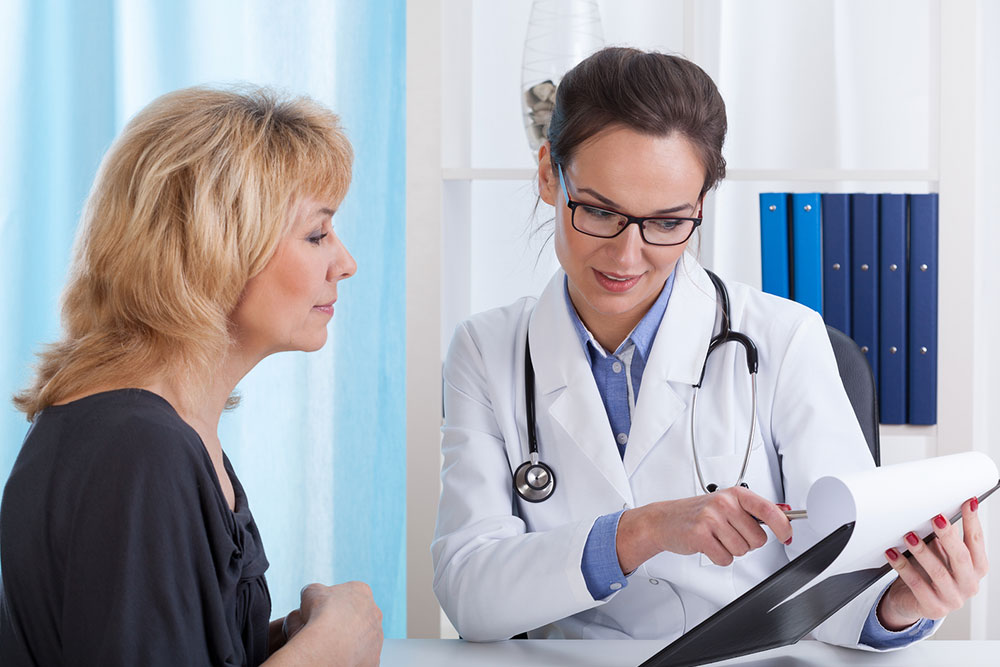
Acute graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a serious complication that can occur after an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. It occurs when the donor’s immune cells recognize the recipient’s tissues as foreign and mount an immune response against them. Acute GvHD typically develops within days following the transplant and can affect multiple organs, primarily the skin, liver, and gastrointestinal tract. The condition is driven by the activation of donor T cells that attack the host’s tissues. Signs of Acute GvHD Skin rashes One of the most common symptoms of acute GvHD is reddened skin areas or rashes. These rashes can resemble sunburns and may cause the skin to be itchy or painful. They can start at the neck, ears, shoulders, or the palms of the hand, and in some cases, they can begin forming at the soles of the feet. As the disease progresses, the rashes can spread to other parts of the body. They can often be accompanied by intense itching, also known as pruritus. The redness and inflammation accompanied by rashes can cause erythema. This can cause blisters and peeling of the skin in intense cases. Gastrointestinal discomfort This is another common sign of the condition to look out for. The patients may experience moderate to severe abdominal pain following the grafting procedure. Some may even have watery or bloody diarrhea along with mucosal damage. Nausea and vomiting resulting from the condition can cause nutritional imbalance, insufficiency, and modified fluid balance. Patients might alternatively have to deal with constipation. It can cause severe bowel obstruction due to a lack of proper bowel movements. Jaundice Acute GvHD also impacts the patient’s liver. The increased bilirubin levels in the patient’s body lead to yellowing of the eyes, nails, and skin. Aside from bilirubin, there is also an observed elevation in the levels of other liver enzymes.