Health
4 surprising facts about menopausal night sweats
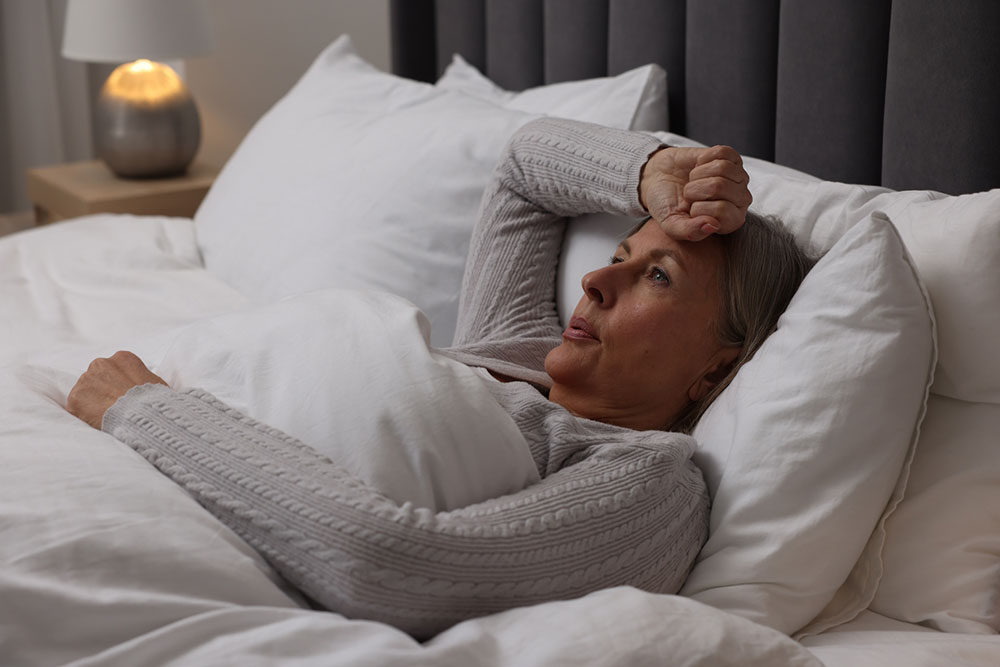
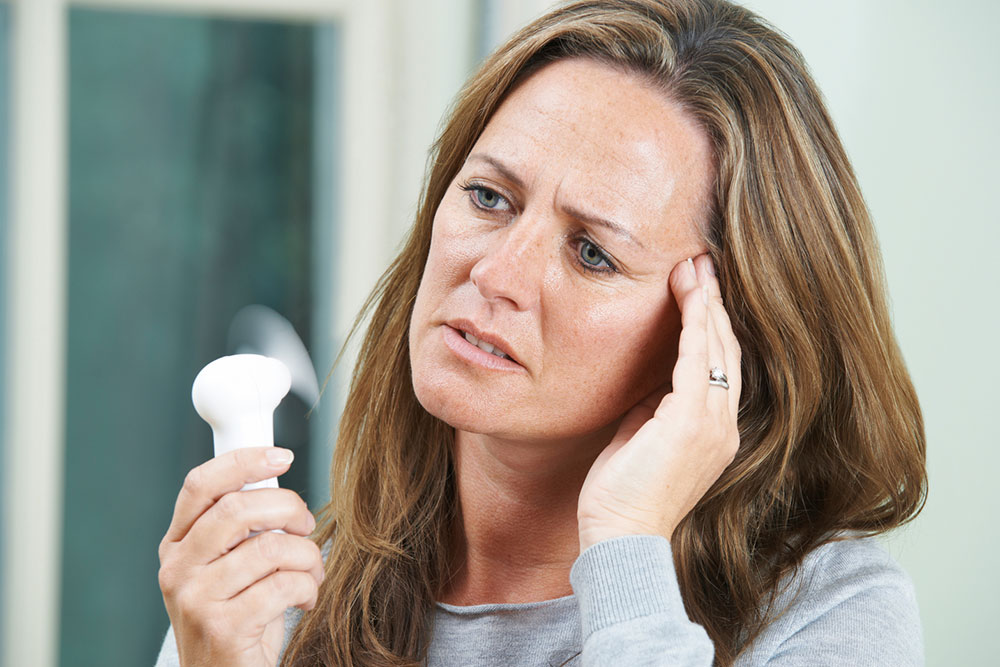
Menopause is a phase following the last menstrual cycle. It is a result of a natural decline in reproductive hormones, which typically happens as women reach their 40s and 50s. There are many symptoms associated with menopause, and night sweats are common in this period. It is essential to recognize and address this symptom and manage it. So, here are some surprising facts about menopausal night sweats one should know. 1. Night sweats may differ from hot flashes Research presented at the North American Menopause Society on the findings of night sweats and hot flashes suggested that night sweats may cause a higher level of stress and discomfort than hot flashes. Further, hot flashes could occur during the day or night but typically have shorter periods of sweating. Night sweats, however, are known to last a lot longer and lead to excessive perspiration. 2. Triggers are not yet known The exact trigger for night sweats remains unknown. It could be triggered due to declining estrogen levels, but there is not enough evidence to establish the link conclusively. Some believe that when the ovaries stop producing estrogen, there is an increase in the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which sets off the brain neurons that help control the body’s temperature. This may lead to night sweats as well as sleep deprivation associated with menopause. 3. Night sweats may last 10 years About 75% of those who go through menopause may experience night sweats and hot flashes. However, some women may start experiencing these symptoms years before their last menstrual cycle. Anecdotal evidence also suggests that some in their 80s continue to experience night sweats. 4. Menopausal night sweats can be managed Although menopause-induced night sweats may not have a cure, there are ways to deal with this symptom. Here are a few things one can try: