Health
Lung cancer – Causes, symptoms, and management
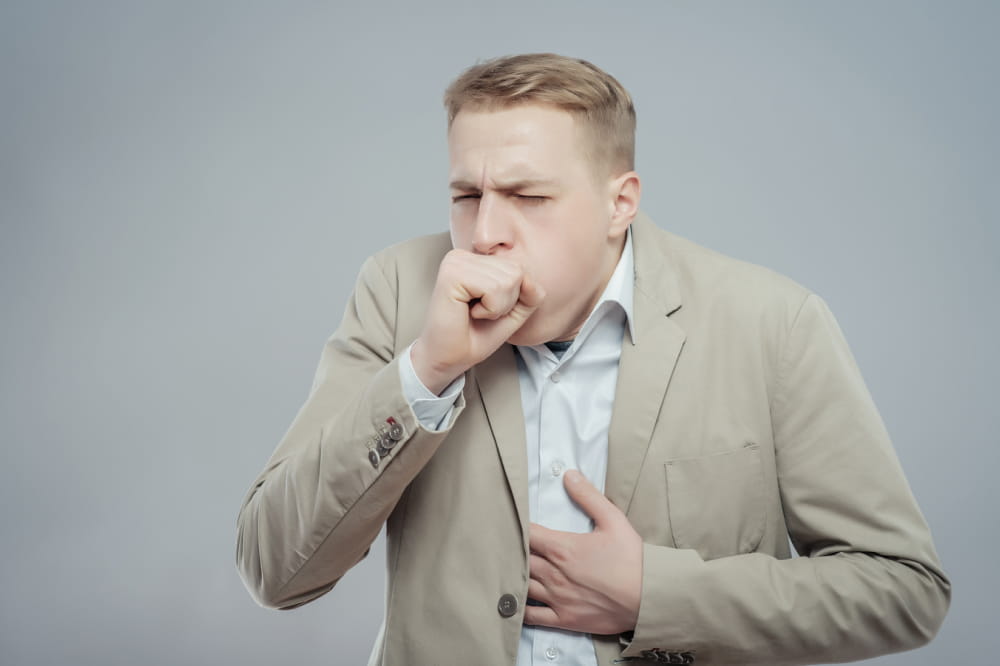
Cancer is triggered due to an uncontrolled multiplication of healthy cells in the body that affects vital organs and functions. Lung cancer is detected when these cells mutate, affecting the lung’s ability to absorb oxygen. It is a progressive disorder and cannot be completely cured. The risk is high among patients exposed to elements that worsen the cancer progression. Here is an overview of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for lung cancer. Causes of lung cancer Exposure to pollutants Exposure to known pollutants and carcinogens is one of the significant risk factors associated with lung cancer. Pollutants comprise chemicals and particulate matter that damage the air sacs in the lungs. This comprises the ability of the lungs to absorb oxygen. Radon gas Radon is one of the most severe triggers of lung cancer. Exposure to this gas is quite common in residential homes as this compound is naturally present in the soil. Over time the gasses creep up into the building’s foundation and leak inside the home. Since this is a colorless, odorless gas, it’s quite difficult to identify this risk without smoke and gas detectors. Genes Certain genetic conditions or mutations in the genome sequence can also trigger lung cancer, especially if there is a history of the condition diagnosed among close members. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of lung cancer will vary depending primarily on the stage of its progression. Persistent cough A persistent cough that worsens over time could indicate lung tissue damage due to cancer. Coughing can also result in tissue damage that triggers bleeding. So, coughing up blood with mucus is another sign to look out for with developing lung cancer. Shortness of breath Breathlessness is another symptom that develops as the lungs cannot absorb oxygen efficiently, forcing the organ to work overtime. As a result, one might frequently gasp for bouts of air to fill up the lungs efficiently.